As the trend toward engaging students in social media content creation in educational settings continues upward, a number of schools are integrating research-backed educational practices. Here’s a look at common strategies and how they can be included in the social media programs that involve students using Class Intercom.
Apply Knowledge
Creating social content provides students opportunities to engage in real-world situations, problems, and tasks within authentic contexts. In doing so, they develop a deeper understanding of rhetoric, storytelling, writing, editing, digital media, design, and other key concepts.
Utilize Authentic Assessment
With the right systems and controls in place, educators can evaluate students’ knowledge, skills, and abilities in the context of social posts for various channels. This provides meaningful real-world context where they can demonstrate their skills through practical tasks and execution.

A student practices their photography skills during a live student social media competition.
Encourage Collaboration
Technology can ensure that social media content planning, creation, and execution is a fundamentally collaborative process that includes multi- step processes with active participation, interaction, and cooperation among students. This fosters a sense of shared responsibility and helps them tap into each other’s strengths and diverse perspectives.
Build Self-Efficacy
Students’ beliefs about their capabilities greatly influence their motivation, effort, and achievement. This means social media can be an environment that fosters confidence and interest in social media outside the classroom can seamlessly translate with the right tools and systems.
Engage with Locally & Globally Relevant Content
The best social media content has local and global relevance, and when students engage with it, they are more likely to understand and retain information, develop critical thinking skills, and apply knowledge effectively.
Offer Choice & Autonomy
Content moderation allows educators to provide students opportunities to make decisions about the content they pursue and create, giving them a sense of ownership and control over their educational experience and allowing them to explore their interests and strengths.
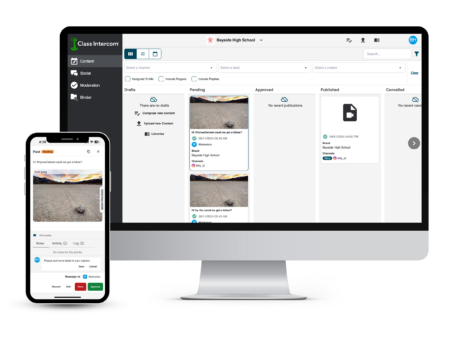
Class Intercom is a comprehensive social media management tool made specifically for schools and school districts, making it easy for educators to leave comments for students directly in the platform.”
Provide Feedback
Notes and workflow tools allow educators and administrators to give guidance to learners about their performance, progress, or understanding of storytelling, design, writing, editing, media management, and other key areas. This feedback loop supports learning by highlighting strengths and areas for further improvement.
Present Multiple Exposures
While every post is unique, social media content creation relies on a number of foundational themes and practices, allowing schools to present learners with the same material or concepts multiple times over a period of time. This enhances learning and retention by reinforcing knowledge through repeated exposure.
Incorporate Reflection & Metacognition
With opportunities to publish work that engages the school community in broader ways, schools promote deep learning and enhance students’ ability to think critically. At the same time, content creation invites creativity, helping students self-regulate their learning process and become more independent learners.
Release Responsibility
When students are safely empowered to collaborate and contribute meaningful content to their school’s socials, educators shift instructional responsibility, while maintaining moderation control and oversight. At the same time, they continue to provide direction and feedback.
Student Social Media Content Creation Backed by Research-Based Strategies
What does the implementation of research-based educational strategies alongside social media content creation look like in practice? Schools have built out content creation teams in a number of ways depending on interest, programming, and administrative support. Some have implemented social media clubs while others have charged journalism, yearbook, and English classes with capturing content. Still others have launched classes geared specifically toward digital media and storytelling, with social media integrated into curriculum. In these circumstances, providing students with securely moderated access to their school’s social media and opportunities to create content becomes a real-world learning opportunity. With the right curricular pieces in place, students learn about social media within the context of themes like storytelling, skill building, student voice, digital citizenship, and community building.
In addition to having an opportunity to deploy some of the aforementioned research-based educational strategies, student content creators also report gaining skills and experience in numerous areas. The most commonly observed student outcomes were: improved design, photography, and photojournalism skills; increased engagement in activities and clubs; increased classroom engagement; increased awareness of marketing and branding; increased interest in media-related education and career paths; and improved written communication and storytelling skills.
Other outcomes reported by survey respondents included: improved digital citizenship; and increased awareness of advocacy, current events, and other timely campaigns and issues. These results align closely with bigger-picture goals like storytelling, student voice, skill building, community, and digital citizenship.
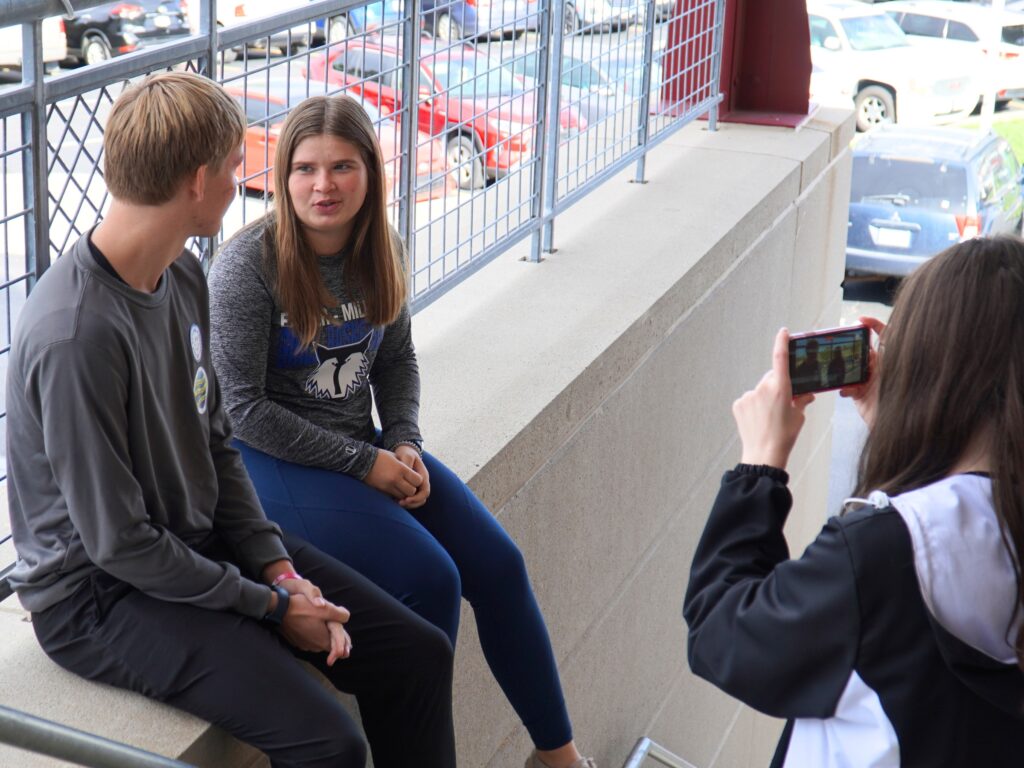

Students create content for school social media at the 2023 Content Generation Workshop.
Interested in adopting student content creation blacked by powerful pedagogy? Class Intercom can help. Follow the link below to get in touch.
This content was originally published as part of the 2024 Social Media in Education Report. Released annually from Class Intercom, the report pulls together survey data from across the education sector to provide key insights and information about how schools are using, managing, and reporting on social media and the technology and workflow infrastructure surrounding social media in an education setting. Download the report here.
